Where does the radon in my home come from?
The radioactive noble gas radon-222 poses a health risk, especially in closed rooms, apartments and houses.
Radon can cause lung cancer if exposed to elevated and highly elevated levels for many years. But how does radon get into buildings in the first place, and why is it so dangerous there?
Here you will find explanations and answers to the most pressing questions.
- Radon is everywhere in the soil
- Why is radon becoming dangerous for humans now of all times?
- The entry paths of radon into buildings
- More radon sources in the building
- Which buildings are affected by radon?
- Renovated old buildings are radon traps
In addition, we will show you why a radon measurement is the first step in reducing the health risk of radon to yourself and your family in your own home.
Radon is everywhere in the soil
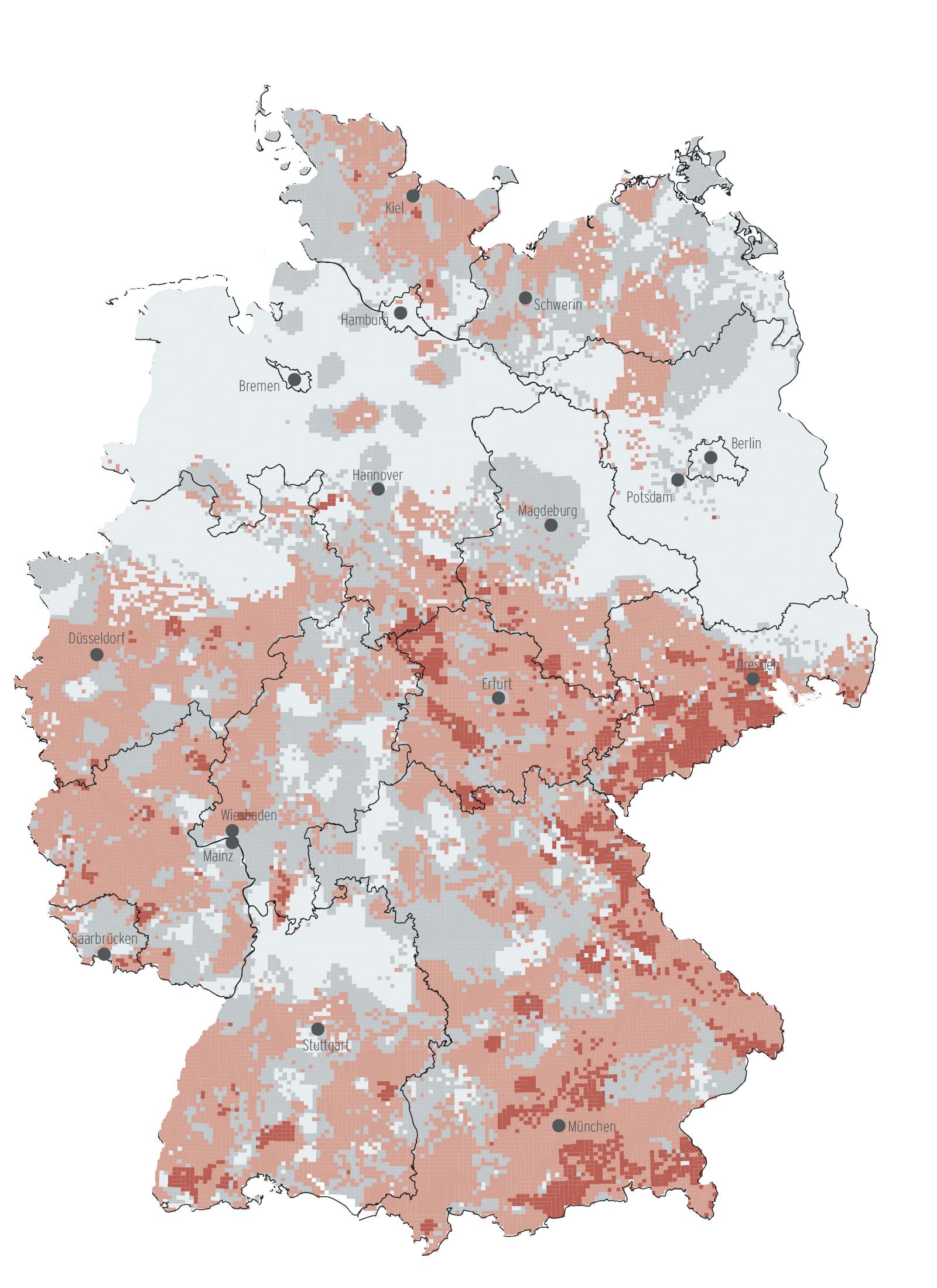
Radon is formed during the radioactive decay of uranium and is thus a naturally occurring noble gas in the soil. It is unevenly distributed all over the world. The soil gas map of the BfS gives an impression: the darker the coloring, the higher the radon activity concentration in the soil gas. In general, radon exposure is elevated in former mining and/or mountainous regions. Also large uranium deposits or porous rock undergrounds can be indications of an extraordinary radon load.
In the open air, the radioactive noble gas mixes with the ambient air and poses no health risks to humans. It is different when radon accumulates in closed indoor spaces.
Why is radon becoming dangerous for humans now of all times?
The lifestyle of modern man is a major contributor to the increase in health exposure to radon. We spend our daily lives predominantly indoors. Even sports many have shifted to the gym or gyms.
Due to Corona and the associated lockdown measures, we spend even less time outside. This also increases the amount of time we are exposed to potentially elevated radon levels.
The entry paths of radon into buildings
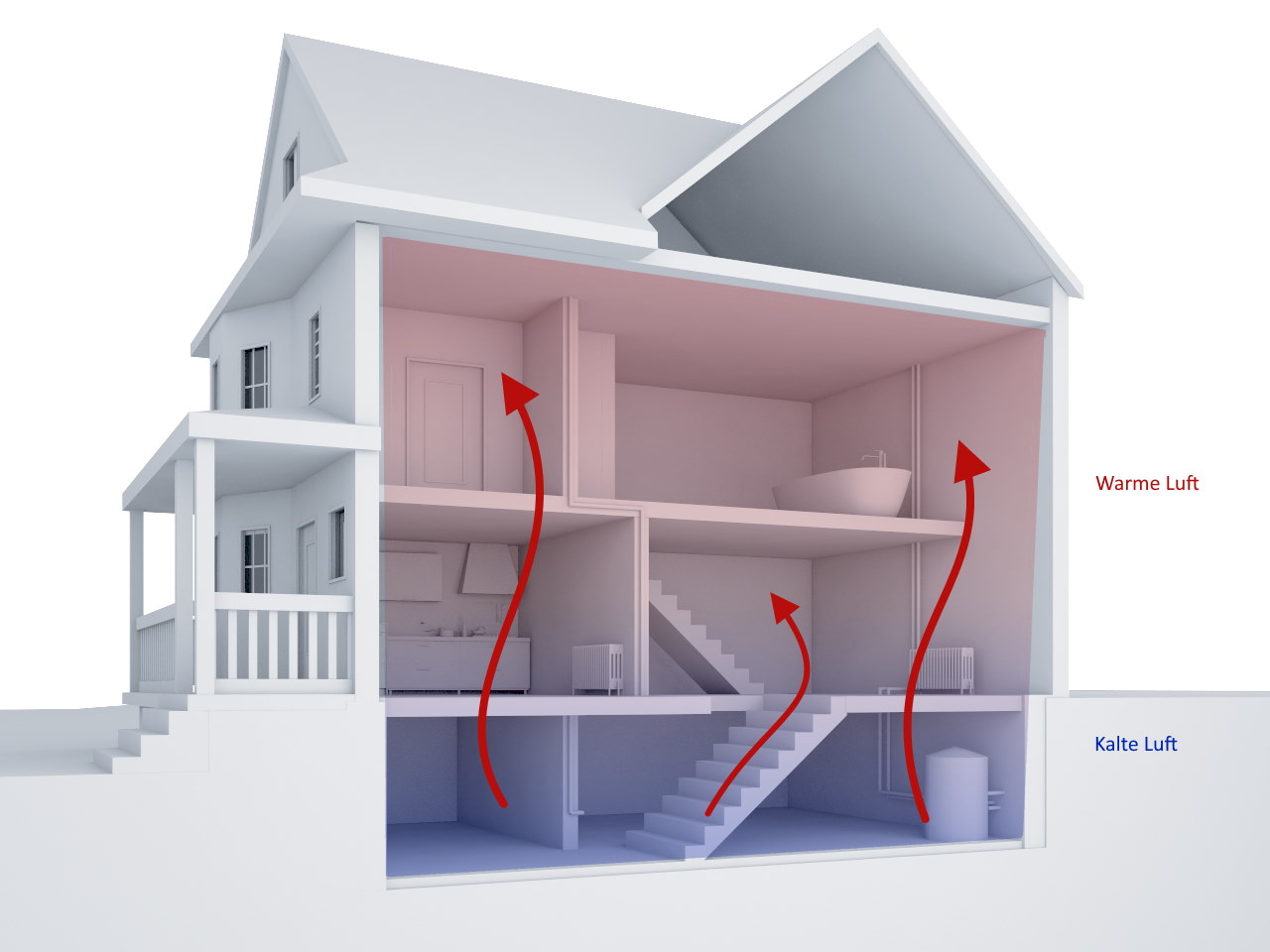
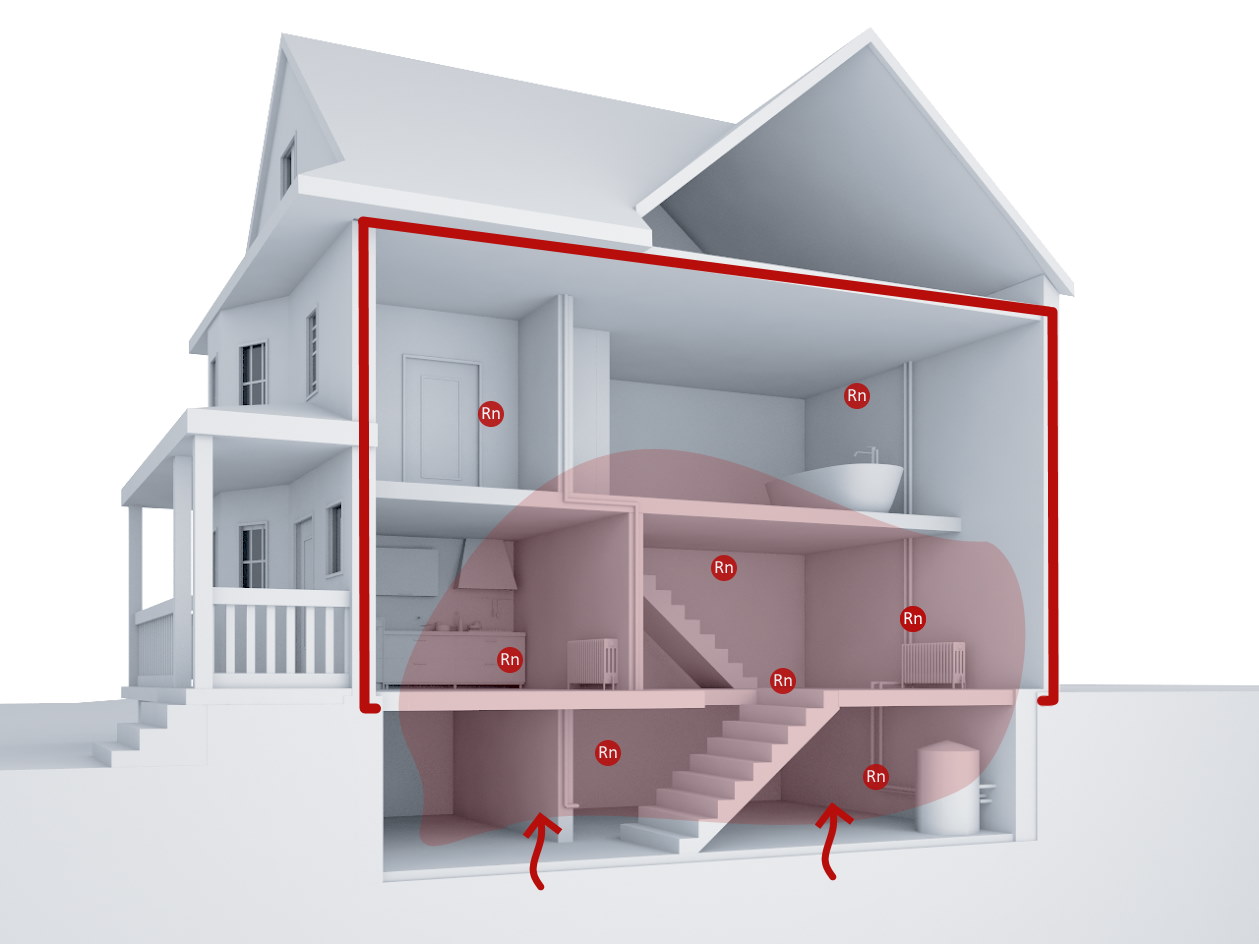
Radon finds a variety of pathways into a home. Because radon rises upward from the soil, most of the entry pathways of radon into a building are found in the basement:
⦁ Cracks in the floor slab
⦁ Leaky joints between the floor slab and walls
⦁ Diffusion through building materials
⦁ Leaking cable and pipe entries
Radon accumulates in the lower rooms (basement, first floor). Due to the so-called chimney effect caused by open windows or heated rooms, radon spreads to the upper floors via stairwells, cable shafts and leaky false ceilings.
More radon sources in the building
However, radon can enter the house not only through leaks. Other possibilities are:
Drinking water: The water-soluble radon is also contained in drinking water. When showering, for example, the radon can outgas. The increased radioactivity is often clearly measurable after showering.
Building materials: Mineral building materials such as natural stone or slag fills in faulty soils contain large amounts of radioactive isotopes. The decay of radium-226 produces radon-222.
Both building materials and drinking water can significantly increase radon exposure in a building. However, radon usually enters the interior of a building through the soil.

Which buildings are affected by radon?
It is difficult to predict which types of buildings are more likely to be affected by radon. Radon occurs practically everywhere and can be encountered in new buildings as well as in old buildings, schools or kindergartens. However, buildings with cracks in the building envelope or a leaky floor slab are generally particularly unsafe for radon ingress. If you find natural soil in your basement or if the basement consists of natural stones, then a radon measurement makes sense in any case.
Renovated old buildings are radon traps
Insulated windows, insulated roofs and freshly plastered facades are the serious reasons why radon contamination can be particularly high in old and existing buildings that have been renovated to improve energy efficiency. While structural renovation measures usually focus on reducing energy consumption and saving heating costs, the basement area in contact with the ground is usually neglected and remains unchanged. Radon continues to penetrate the building unhindered underground, but is much more difficult to escape above ground from the building, which is insulated all around. Ventilation reduces the radon load in the short term, but in some cases, especially during the heating period, it is no longer sufficient.

A radon measurement is the first step
Measures to protect against radon are many and not all are equally suitable. Before you invest unnecessary money in a radon remediation, first start with a radon measurement. First determine if there is any radon exposure in your home at all and to what degree. Based on this data, make a serious decision, appropriate to the situation, as to whether further measures are necessary and, if so, which ones.
With our Radon consultant to Radon measurements, we are at your side with advice and measuring equipment, so that you can quickly get a concrete overview of the possible radon exposure in your building. Stop by and take the first step towards a radon safe home.
Many information options around Radon!
You still have questions about radon, its origin or measures to reduce the health risk? Use the manifold information possibilities of the Radon Shop.
Radon Helpdesk
An overview of individual approaches to radon, as well as basic information on the three measures: measurement, ventilation and remediation.
Radon Encyclopedia
Useful definitions of terms, legal texts, and physical and chemical relationships explained in a comprehensible way.
Phone
Talk to one of our three radon specialists: +49 9076 - 91 99 835
